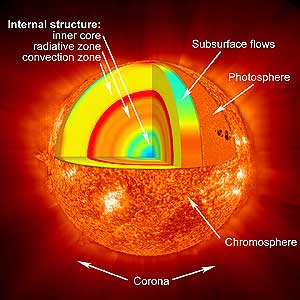
The internal structure of the sun is composed of three parts,
1. The Energy Core
2. The Radioactive Zone
3. The Convective Zone.
The Energy core is where the hydrogen undergoes Fusion to produce Helium at enormous temperatures and pressures. The energy core extends to about 0.25 of the Solar radius from the centre of the sun.
The radioactive zone is the zone through which the energy produced travels outward through radiative diffusion. It can take a very long time( thousands or millions of years) for the energy to come out of this zone.
The convective zone is a opaque region with a relatively low temperature and energy travels mainly through convection.
*Moving outwards from the centre to the surface of the sun, The temperature decreases, the density decreases, the mass percentage increases and the luminosity increases.
A lot of information regarding the sun such as pressures, densities, chemical compositions and rotation rates can be inferred by studying the vibrations of the sun. The study of the vibrations of the sun is called Helioseismology.
The Sun's atmosphere
The sun's atmosphere has three main parts,
1 Photosphere (innermost)
2 Chromosphere (above photosphere)
3 Corona (outermost)
Everything below the atmosphere is called the Solar interior.
Photosphere
The Photosphere is the visible surface of the sun. Because of its opaqueness, photons emitted below the photosphere cannot escape. The temperature decreases outwards of the photosphere. Since when viewing the Sun, we see deeper through the photosphere than when looking at the centre of the sun, The edges of the sun appear dimmer. This is called the Limb Darkening effect. The convection currents in the photosphere gives rise to what is known as "Granules" These granules are formed in a cyclic manner and are roughly about 1000km in size.
Chrmosphere
Chromosphere means "Sphere of Colour" and it consists of gases less denser than that of the Photosphere. Since the light of the chromosphere mainly consists of the red emission line of Hydrogen, H-alpha, The chromosphere is clearly seen through a telescope equipped with a H-alpha filter. On observation of the Chromosphere, thin columns of hot gas jets can be seen. These gas jets are called "Spicules". Spicules rise from the boundaries of large granules.
Corona
The corona is the outermost of the Solar atmosphere, has a very low density and a very high temperature (millions of degrees). This low density and high temperature of the corona makes it almost invisible, however it is seen spectacularly as a bright ring in a full solar eclipse. The corona extends to several million km from the surface of the sun. Sometimes gases escape to outer space from the Sun through regions with cooler gases called "Coronal Holes" This escaping gases form what is known as the "Solar Wind".
The Sun's Magnetism
The most common type of Solar magnetic activity are Sunspots. Sunspots are relatively cooler regions in the Sun which is why they appear darker than the rest of the sun due to the lower amount of radiation emitted. Sunspots are areas of concentrated Magnetic field. This is proved using the Zeeman Effect. Occurrence of Solar Prominences and Flares are also related to Sunspots.
It has been observed that the average number of Sunspots increase and decrease in a cycle of 11 years. with the polarity of the Sun changing every 11 years. i.e the Magnetic poles of the Sun Change every 11 years giving rise to a 22year magnetic cycle.
It is known that the differential rotation of the sun gives rise to its magnetic field and its properties. Thus the solar cycles are caused by the differential rotation of the Sun.


 Modern Astronomy can be classified into three major periods
Modern Astronomy can be classified into three major periods
 observe the skies better.
observe the skies better.
